Binary Search Tree
BST是有顺序的,一般是左小右大,而普通的二叉树妹有顺序 BST 中序遍历的时候,如果先左后右就是升序排序结果,先右后左就是降序 template for all BST situations
void BST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root.val == target)
// 找到目标,做点什么
if (root.val < target)
BST(root.right, target);
if (root.val > target)
BST(root.left, target);
}
遍历BST
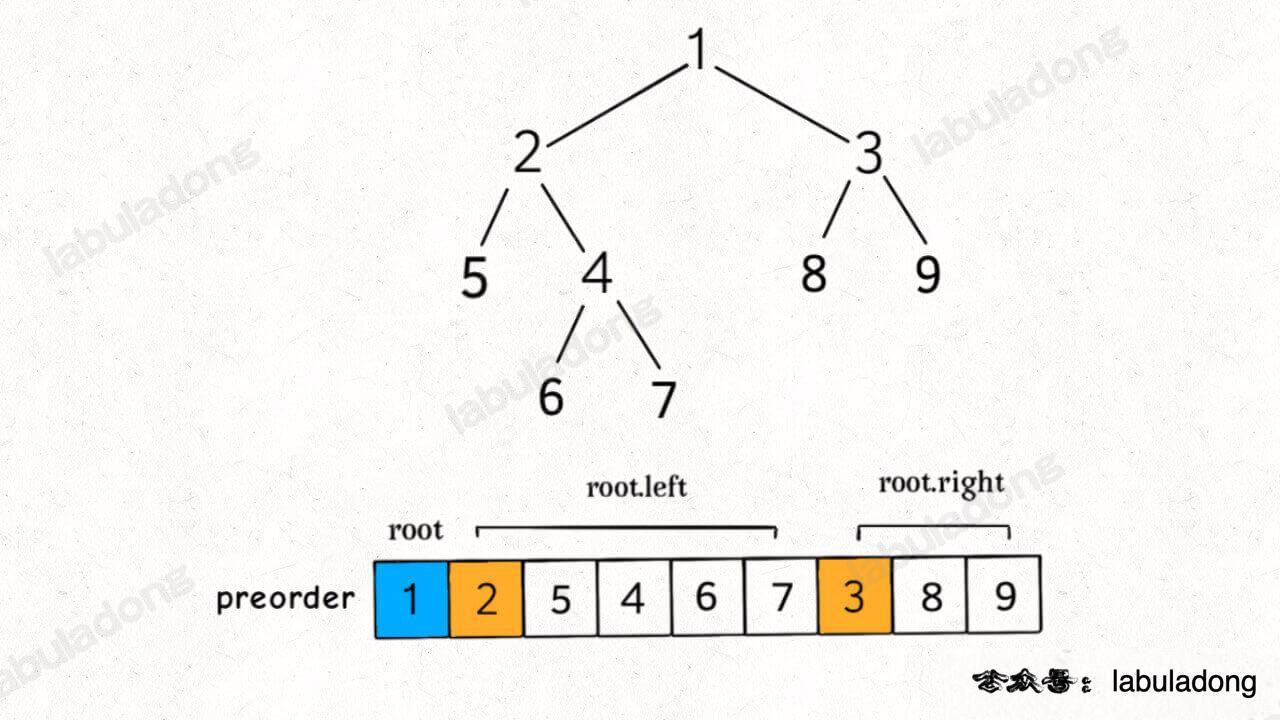
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
print(root.val);// 前序遍历
traverse(root.left);
print(root.val);// 中序遍历
traverse(root.right);
print(root.val);// 后序遍历
}
第k小的元素
int counter = 0; // 记录一个遍历counter
int result; // 记录结果
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
traverse(root, k);
return result;
}
void traverse(TreeNode root, int k) { //中序遍历
if (root == null) return;
traverse(root.left, k); // 左小
counter++;
if(counter == k){
result = root.val;
}
traverse(root.right, k); // 右大
}
累加树
TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root);
return root;
}
int sum = 0;
void traverse(TreeNode root) { //中序遍历
if (root == null) {
return;
}
traverse(root.right);// 先遍历右边,因为右边存着更大的值,当前值需要的是比他还大的值
sum += root.val;
root.val = sum;
traverse(root.left);
}
是不是BST
boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root){
return isValidBST(root, null, null);
}
boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, TreeNode min, TreeNode max) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
if(min != null && min.val >= root.val){
return false;
}
if(max != null && max.val <= root.val ){
return false;
}
return isValidBST(root.left, min, root) && isValidBST(root.right, root, max);
// 所有的左节点必须小于root,所有的右节点必须大于root, 等于也不行
}
搜索二叉树
//用到了二叉树的二分查找
TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(target > root.val){
return searchBST(root.right, target);
}
if(target < root.val){
return searchBST(root.left, target);
}
return root;
}
插入
TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val); // 找到空位,插入新节点
if (root.val < val)
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val); //给root的右边换成更大的值
if (root.val > val)
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val); //给root的左边换成更大的值
return root;
}
删除
TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root.val == key) { // found,删除
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) //is leaf node, just delete
return null;
if (root.left == null) // left is empty, let it's right branch take it's place
return root.right;
if (root.right == null) // right is empty, let it's left bracnh take it's place
return root.left;
if (root.left != null && root.right != null) { // both branch occupied
TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right);
// 删除右子树最小的节点
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val); // 用右子树最小的节点替换 root 节点
minNode.left = root.left;
minNode.right = root.right;
root = minNode;
}
} else if (root.val > key) { // Search left
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if (root.val < key) { // Search right
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
TreeNode getMin(TreeNode node) {
while (node.left != null) { // BST 最左边的就是最小的
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
穷举二叉树可能组合的数量
int[][] possibility;
int[][] memo;
int numTrees(int n) {
memo = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
return count(1, n);
}
int count(int lo, int hi) { // [lo, hi]区间的BST个数
if(lo > hi){ //base case
return 1;
}
if(memo[lo][hi] != 0){
return memo[lo][hi]; // 已经存在,不计算直接返回
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) { // 用每一个值做为root
int left = count(lo, i-1);
int right = count(i+1, hi);
result += right * left; //左边的可能性 x 右边的可能性就是以i为root的全部可能性
}
memo[lo][hi] = result;
return result;
}
穷举可能性
List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n){
return build(1, n);
}
List<TreeNode> build(int lo, int hi){
List<TreeNode> result = new LinkedList<>();
if (lo > hi) { // base case
result.add(null);
return result;
}
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) { // 用每一个值做为root
//建立左右子树的所有可能的BST。
List<TreeNode> leftTree = build(lo, i-1);
List<TreeNode> rightTree = build(i+1, hi);
//遍历每一种左右子树的组合,添加到一个列表里,这个列表会被返回到上一次递归让他再加上自己的root,变成上上个的左右子树
//这里的拼接只限于两层,root层和左右子树的那一层
for (TreeNode left : leftTree) {
for (TreeNode right : rightTree) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(i); // i作为root
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
result.add(root);
}
}
}
return result;
}